To set up and smoothly use Apache2 and MySQL on Linux without XAMPP, follow these steps:
sudo apt updatesudo apt install apache2 -ysudo systemctl enable apache2
sudo systemctl start apache2Verify Apache2 installation: Open a browser and visit http://localhost. You should see the Apache2 default page.
1. Install MySQL server:
sudo apt install mysql-server -y2. Secure MySQL installation:
sudo mysql_secure_installationFollow the prompts to set up a root password and secure the installation.
3. Verify MySQL installation:
sudo systemctl status mysqlEnsure it’s active and running.
1. Install PHP and required extensions:
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql php-cli php-curl php-gd php-xml -y2. Test PHP integration with Apache:
/var/www/html/: sudo nano /var/www/html/info.php<?php
phpinfo();
?>http://localhost/info.php in a browser.1. Set up a Virtual Host for WordPress or Laravel:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/your_project.confAdd the following:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName your_project.local
DocumentRoot /path/to/your/project/public
<Directory /path/to/your/project/public>
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>2. Enable the site and restart Apache:
sudo a2ensite your_project.conf
sudo systemctl restart apache23. Edit /etc/hosts to map your domain:
sudo nano /etc/hosts Add: 127.0.0.1 your_project.localsudo apt install composercomposer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel your_project1. Install phpMyAdmin:
sudo apt install phpmyadmin2. Integrate phpMyAdmin with Apache:
sudo ln -s /usr/share/phpmyadmin /var/www/html3. Access phpMyAdmin: Visit http://localhost/phpmyadmin in your browser.
sudo systemctl restart apache2sudo systemctl restart mysqltail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log"Manage Multiple WordPress (or other) Projects on Apache2"
To manage multiple WordPress (or other) projects on Apache2, you should organize your files and configure Apache to serve each project separately. Here's a step-by-step guide:
1. Directory Structure for Projects
Create a dedicated folder for your projects under
/var/www/. For example:Bashsudo mkdir -p /var/www/project1 sudo mkdir -p /var/www/project2 sudo mkdir -p /var/www/project3You can name the folders as per your project names.
2. Place WordPress Files
Download and extract WordPress into each project folder:
Bashcd /tmp wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz tar -xvf latest.tar.gzCopy WordPress files to each project directory:
Bashsudo cp -r wordpress/* /var/www/project1/ sudo cp -r wordpress/* /var/www/project2/ sudo cp -r wordpress/* /var/www/project3/
3. Set Correct Permissions
Set the correct ownership and permissions for your project directories:
Bashsudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/project1 sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/project2 sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/project3 sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/
4. Configure Virtual Hosts
Create a separate Virtual Host configuration file for each project. For example:
Project 1:
Bashsudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/project1.confAdd the following content:
Bash<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName project1.local DocumentRoot /var/www/project1 <Directory /var/www/project1> AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/project1_error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/project1_access.log combined </VirtualHost>Project 2:
Bashsudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/project2.confAdd similar content, changing the
ServerNameandDocumentRoot:Bash<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName project2.local DocumentRoot /var/www/project2 <Directory /var/www/project2> AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/project2_error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/project2_access.log combined </VirtualHost>Repeat for Project 3, etc.
5. Enable Virtual Hosts
Enable each configuration using
a2ensite:Bashsudo a2ensite project1.conf sudo a2ensite project2.conf sudo a2ensite project3.confReload Apache to apply changes:
Bashsudo systemctl reload apache2
6. Update
/etc/hostsfor Local DomainsEdit the hosts file to map your project domains to
localhost:Bashsudo nano /etc/hostsAdd the following lines:
Bash127.0.0.1 project1.local 127.0.0.1 project2.local 127.0.0.1 project3.local
7. Access Your Projects
- Open a browser and navigate to:
http://project1.localfor Project 1http://project2.localfor Project 2http://project3.localfor Project 3
If phpMyAdmin is not installed, follow these steps to install it:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install phpmyadmin -y
During the installation, you'll be prompted to choose a web server. Select Apache2 using the spacebar and press Enter.
After installation, ensure that phpMyAdmin is properly linked to Apache:
sudo ln -s /usr/share/phpmyadmin /var/www/html/phpmyadminsudo systemctl restart apache2Visit http://localhost/phpmyadmin in your browser. You should see the phpMyAdmin login page
Here’s how to create a new MySQL user, set a password, and grant database access:
Open your terminal and log in to MySQL as the root user:
sudo mysql
To create a new user, run the following SQL command:
CREATE USER 'new_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'user_password';
new_user with the desired username.user_password with a strong password.If you want the user to have access to a specific database (e.g., example_db):
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON example_db.* TO 'new_user'@'localhost';
This gives the user full access (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc.) to the example_db database.
If you want the user to have access to all databases:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'new_user'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Make sure to reload the privileges to apply the changes:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Once done, exit the MySQL prompt:
EXIT;
You can test the new user by logging in:
mysql -u new_user -p
Enter the password you set (user_password) when prompted. If successful, the new user is ready to use.
To check and change the password policy in MySQL, follow these steps:
Open a terminal and log in as the root user:
sudo mysql
Run the following query to check the current password policy settings:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'validate_password%';
This will display several settings, including:
validate_password.policyvalidate_password.lengthvalidate_password.mixed_case_countvalidate_password.number_countvalidate_password.special_char_countThe validate_password.policy variable controls the strength of the password. It has three levels:
MEDIUM plus checks dictionary words.You can adjust the policy and other requirements:
To set a specific policy level:
SET GLOBAL validate_password.policy = 'LOW'; -- Change to LOW, MEDIUM, or STRONG
To change the minimum password length (default is 8):
SET GLOBAL validate_password.length = 12; -- Change to your desired length
SET GLOBAL validate_password.mixed_case_count = 1; -- Require at least 1 uppercase and 1 lowercaseSET GLOBAL validate_password.number_count = 1; -- Require at least 1 numberSET GLOBAL validate_password.special_char_count = 1; -- Require at least 1 special characterRun this query again to confirm the new settings:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'validate_password%';To ensure these settings persist after a server restart, edit the MySQL configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnfAdd the following lines under the [mysqld] section:
validate_password.policy=MEDIUM
validate_password.length=12
validate_password.mixed_case_count=1
validate_password.number_count=1
validate_password.special_char_count=1
Save and close the file, then restart MySQL:
sudo systemctl restart mysql
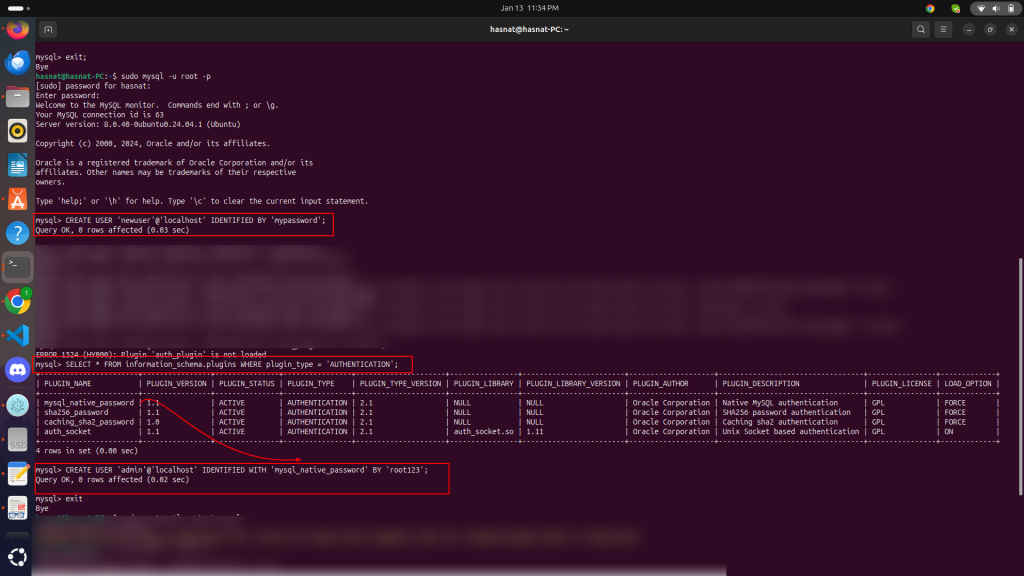
The error ERROR 1524 (HY000): Plugin 'auth_plugin' is not loaded indicates that the specified authentication plugin (auth_plugin) is not enabled or installed in your MySQL server.
SELECT * FROM information_schema.plugins WHERE plugin_type = 'AUTHENTICATION';This will show you the plugins available on your MySQL server, such as mysql_native_password, caching_sha2_password, etc.
2. Use a valid authentication plugin
Choose an appropriate plugin from the list and update your command. For example:
mysql_native_password is available: CREATE USER 'admin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH 'mysql_native_password' BY 'root123';caching_sha2_password is available: CREATE USER 'admin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH 'caching_sha2_password' BY 'root123';3. Ensure the plugin is loaded
If the required plugin is not loaded, you may need to configure it in your MySQL configuration file (my.cnf or my.ini) and restart the MySQL server.
Add the following under the [mysqld] section:
plugin-load-add=auth_plugin_name.so Replace auth_plugin_name with the desired plugin, such as mysql_native_password.
4. Restart MySQL
After making changes to the configuration file, restart the MySQL server:
sudo systemctl restart mysql